Electric Vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular as more people embrace sustainable transportation options. However, one aspect of EV ownership that can be a bit confusing is the multitude of charging connector types used around the world. Understanding these connectors, their implementation standards, and available charging modes is crucial for hassle-free charging experiences.
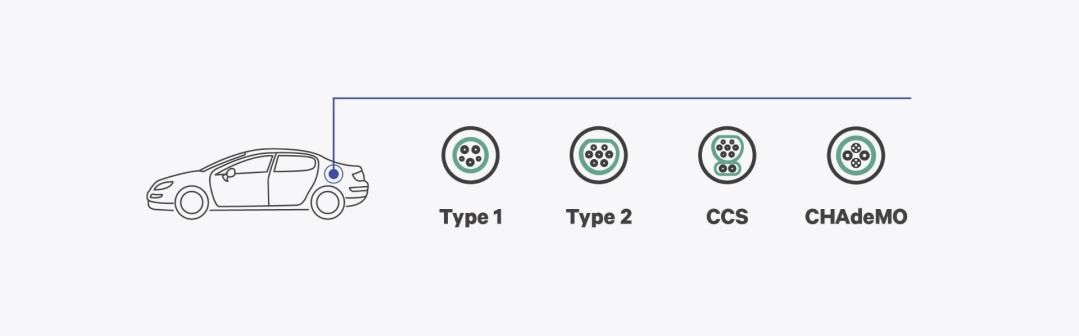
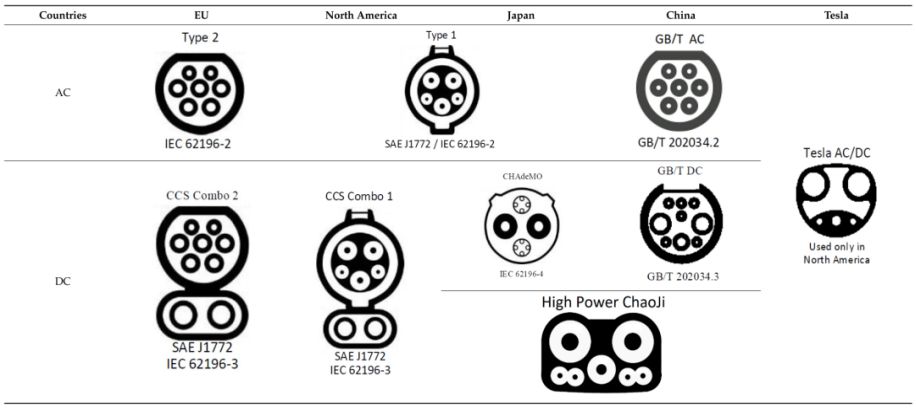
Different countries worldwide have adopted various charging plug types. Let's delve into the most common ones:
There are two types of AC plugs:
Type1 (SAE J1772): Primarily used in North America and Japan, type 1 connectors feature a five-pin design. They are suitable for both AC charging, delivering power levels of up to 7.4 kW on AC.
Type2 (IEC 62196-2): Dominant in Europe, type 2 connectors come in single-phase or three-phase configurations. With different variants supporting various charging capacities, these connectors enable AC charging ranging from 3.7 kW to 22 kW.
Two types of plugs exist for DC charging:
CCS1 (Combined Charging System, Type 1): Based on the type 1 connector, CCS type 1 incorporates two additional pins to enable DC fast charging capabilities. This technology can deliver up to 350 kW of power, drastically reducing charging times for compatible EVs.
CCS2 (Combined Charging System, Type 2): Similar to CCS type 1, this connector is based on the type 2 design and provides convenient charging options for European electric vehicles. With DC fast charging capabilities up to 350 kW, it ensures efficient charging for compatible EVs.
CHAdeMO: Developed in Japan, CHAdeMO connectors have a unique design and are widely used in Asian countries. These connectors offer DC fast charging up to 62.5 kW, allowing for quicker charging sessions.
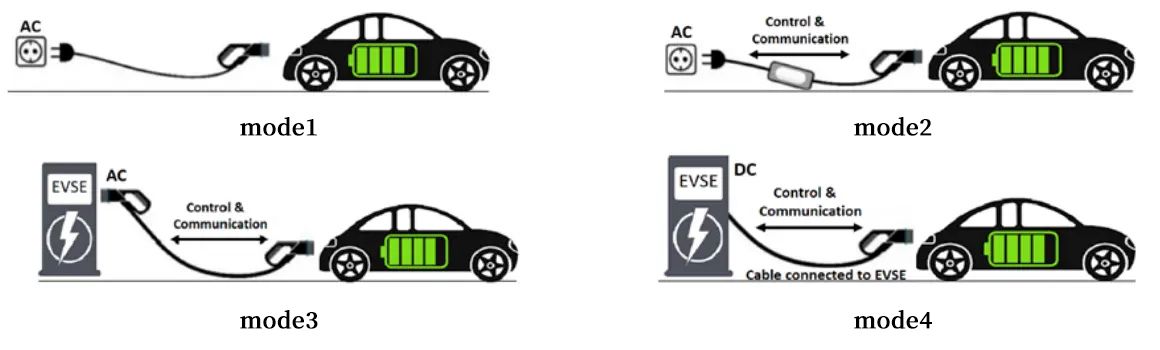
Besides,to ensure compatibility between vehicles and charging infrastructure, international organizations have established implementation standards for EV connectors. Implementations are typically classified into four modes:
Mode 1: This basic charging mode involves charging via a standard domestic socket. However, it offers no specific safety features, making it the least secure option. Due to its limitations, Mode 1 is not recommended for regular EV charging.
Mode 2: Building on Mode 1, Mode 2 introduces additional safety measures. It features an EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment) with built-in control and protection systems. Mode 2 also allows for charging through a standard socket, but the EVSE ensures electrical safety.
Mode 3: Mode 3 revamps the charging system by incorporating dedicated charging stations. It relies on a specific connector type and features communication capabilities between the vehicle and charging station. This mode provides enhanced safety and reliable charging.
Mode 4: Primarily utilized for DC fast charging, Mode 4 focuses on direct high-power charging without an onboard ev charger. It requires a specific connector type for each ev charging station.
Alongside the different connector types and implementation modes, it is important to note the applicable power and voltage in each mode. These specifications vary across regions, affecting the speed and efficiency of EV charging.
As EV adoption continues to increase globally, efforts to standardize charging connectors are gaining momentum. The goal is to establish a universal charging standard that allows seamless interoperability between vehicles and charging infrastructure, regardless of geographical location.
By familiarizing ourselves with the various EV charging connector types, their implementation standards, and charging modes, EV users can make better-informed decisions when it comes to charging their vehicles. With simplified, standardized charging options, the transition to electric mobility becomes even more convenient and appealing for individuals worldwide.
Post time: Sep-18-2023
